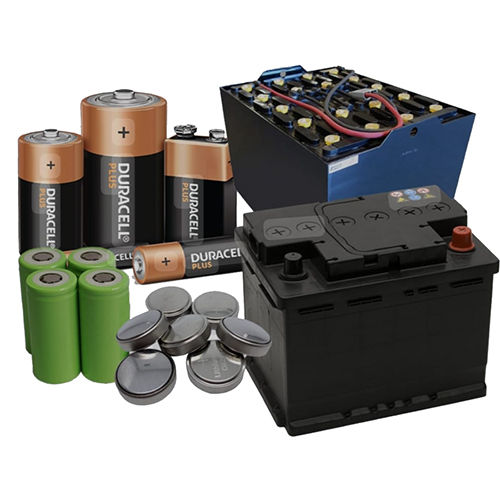
Chargeable Batteries
Chargeable Batteries Specification
- Batteries Type
- Chargeable Batteries
- Cover
- Yes
Chargeable Batteries Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 10 Pieces
- Supply Ability
- 100 Pieces Per Week
- Delivery Time
- 7 Days
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Chargeable Batteries
Introduction: Rechargeable batteries are designed to be used multiple times by recharging them after they are depleted. They are commonly used in devices such as smartphones, laptops, cameras, and various electronic gadgets.
Types of Rechargeable Batteries:
-
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries:
- Characteristics:
- Energy Density: High energy density, allowing for longer battery life in a compact form.
- Voltage: Typically 3.6V to 3.7V per cell.
- Common Uses: Smartphones, laptops, tablets, cameras, and portable electronics.
- Advantages: Lightweight, long lifespan, minimal memory effect.
- Disadvantages: Higher cost, requires protection circuits.
- Characteristics:
-
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries:
- Characteristics:
- Energy Density: Lower than Li-ion but higher than NiCd.
- Voltage: Typically 1.2V per cell.
- Common Uses: Rechargeable AA and AAA batteries for household devices.
- Advantages: Less toxic than NiCd, good capacity, less prone to memory effect.
- Disadvantages: Self-discharge rate is higher, lower energy density.
- Characteristics:
-
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries:
- Characteristics:
- Energy Density: Lower compared to Li-ion and NiMH.
- Voltage: Typically 1.2V per cell.
- Common Uses: Power tools, emergency lighting, and some older electronics.
- Advantages: Durable, good performance in extreme temperatures.
- Disadvantages: Toxic cadmium, pronounced memory effect, lower capacity.
- Characteristics:
-
Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Characteristics:
- Energy Density: Lower than lithium-ion but cost-effective for large applications.
- Voltage: Typically 2V per cell, with common configurations being 6V or 12V.
- Common Uses: Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), solar energy storage.
- Advantages: Low cost, reliable, and durable.
- Disadvantages: Heavy, less efficient, lower energy density.
- Characteristics:
Applications:
-
Consumer Electronics:
- Powering devices such as smartphones, tablets, cameras, and laptops.
-
Portable Gadgets:
- Used in rechargeable flashlights, power tools, and wireless devices.
-
Energy Storage Systems:
- Employed in solar power systems and backup power supplies.
Considerations:
-
Capacity and Voltage:
- Choose a battery with the appropriate capacity (mAh or Ah) and voltage for your device.
-
Charging Requirements:
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for charging to ensure safety and prolong battery life.
-
Environmental Impact:
- Properly recycle batteries to minimize environmental impact.

- Minimum Order Quantity
- 10 Pieces
- Supply Ability
- 100 Pieces Per Week
- Delivery Time
- 7 Days
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email



 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry